nfc reader vs rfid reader RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency . 目前我们大多数银行卡和证件都使用RFID技术储存信息,通过NFC手机或其他 读写器 就可以隔空盗窃,卡片以及个人信息随时都有可能被暴露和传播。. 相对于RFID 防盗钱包,一张屏蔽卡就可以低成本地保护银行卡 信息安全,有效防止盗刷、隐私信息外泄等风险 .
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid nfc reader writer
2 · nfc tag reader used for
3 · nfc rfid reader software
4 · nfc rfid reader app
5 · differences between rfid and nfc
6 · adafruit rfid reader
7 · adafruit nfc reader
Sunday, December 31, 1989NFC: Los Angeles Rams 21, Philadelphia Eagles 7The Rams outgained . See more
rfid vs nfc difference
RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency . RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch .
pso smart card launch
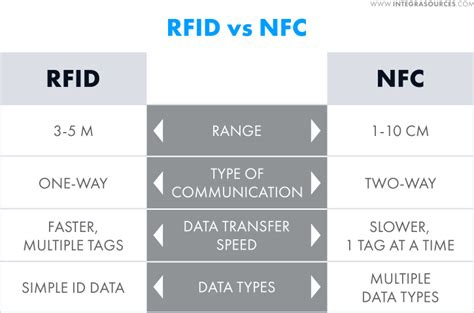
RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in .
NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.
RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-physical technique used to relay information. It relies on smart tags, which are attached to objects like products in stores or animals on a farm. The smart tags work in collaboration with RFID readers, which provide power and receive the relayed identification data.
In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .However, there is a distinction between the two. Unlike RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, NFC tags have the capability to both send and receive information, allowing for two-way communication. In contrast, RFID tags are typically designed for one-way communication. RFID is far more configurable and customizable than NFC. Low-frequency RFID has a small read range, but low-frequency RFID waves can pass through water or metal. High-frequency systems can support ranges of a few inches to a few feet, while ultra-high frequency systems can range 25 feet or more. RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.While both NFC and RFID are based on radio frequency technology, they serve different purposes and possess distinct attributes. In this article, we will delve into the characteristics of NFC and RFID, exploring their similarities and differences.RFID generally supports one-way communication, where the reader sends signals and receives information from tags. In contrast, NFC enables two-way communication, allowing devices to exchange data bidirectionally. This feature makes NFC more suitable for interactive applications.
One of the main differences between RFID and NFC is their reading range. Depending on the operating frequency, the reading range of RFID technology can be extended from a few centimeters to more than ten meters. Compared to RFID, the . Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a non-physical technique used to relay information. It relies on smart tags, which are attached to objects like products in stores or animals on a farm. The smart tags work in collaboration with RFID readers, which provide power and receive the relayed identification data.In peer-to-peer mode, two NFC-enabled devices can exchange data directly, without the need for a central server or intermediary. In reader/writer mode, the NFC device can read and write data to NFC tags, similar to how an RFID reader interacts with .
rfid nfc reader writer
nfc tag reader used for
pki smart card linux
nfc rfid reader software

2017 National Football League Standings. 2017-18 National Football League Teams, Rosters and Statistics 2017-18 National Football League Statistical Leaders. Postseason .
nfc reader vs rfid reader|nfc rfid reader software