rain vs rfid Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID .
We'd like to start by clarifying that you won't see the option to enable NFC scanning .
0 · rain rfid standard
1 · rain rfid reader
2 · rain rfid meaning
3 · rain alliance rfid
4 · rain alliance florence
5 · impinj website
6 · impinj rfid software
7 · impinj rain rfid
$32.00
How does RAIN RFID compare to other RFID technologies from a cost, quality and complexity perspective? What is the return on investment (ROI) for RFID? And these are just the most commonly asked questions.In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read . Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 .
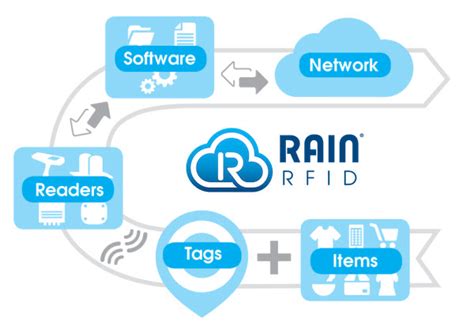
How does RAIN RFID compare to other RFID technologies from a cost, quality and complexity perspective? What is the return on investment (ROI) for RFID? And these are just the most commonly asked questions.In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item with a RAIN tag.Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID . UHF vs. RAIN in a nutshell. The terms RAIN and UHF are often used interchangeably. Labeling a system as RAIN RFID lets the user know that the system or technology adheres to a specific standard and protocol. The RAIN Alliance is the industry organization supporting the universal adoption of RAIN RFID.
UHF RFID is often called RAIN RFID, a name that brands passive UHF RFID products and technologies that adhere to certain industry standards and protocols. NFC, on the other hand, operates at close range, typically around 5 cm . What kind of RFID is RAIN and how does RAIN differ from other types of RFID? RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and . While NFC, RFID and RAIN RFID technology may be similar, they each have clear differences. Learn more about what technology is right for your business! When customers think of paying for their lunch with their phone or smartwatch, it seems like a relatively novel concept.The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to identify and find objects. RFID is a generic term that encompasses different frequencies and standards, including both NFC and RAIN — two technologies supported by industry alliances.We recommend you use the term RAIN instead of, or in addition to, RFID or passive UHF RFID. The more you use it, the more awareness it will create, improving communications between you and the customer.
How does RAIN RFID compare to other RFID technologies from a cost, quality and complexity perspective? What is the return on investment (ROI) for RFID? And these are just the most commonly asked questions.In simple terms, RAIN is a passive, battery-free wireless technology that uses a reader to read and write a tagged item, manage the data, and take action. This enables businesses and consumers to identify, locate, authenticate, and engage with every item with a RAIN tag.Two of the most popular forms of RFID are NFC and RAIN RFID. At 13.56 megahertz, NFC is a high-frequency RFID, while RAIN (whose acronym — a nod to its reach into the cloud — derives from “RAdio frequency IdentificatioN”) is an ultrahigh-frequency RFID .
UHF vs. RAIN in a nutshell. The terms RAIN and UHF are often used interchangeably. Labeling a system as RAIN RFID lets the user know that the system or technology adheres to a specific standard and protocol. The RAIN Alliance is the industry organization supporting the universal adoption of RAIN RFID. UHF RFID is often called RAIN RFID, a name that brands passive UHF RFID products and technologies that adhere to certain industry standards and protocols. NFC, on the other hand, operates at close range, typically around 5 cm . What kind of RFID is RAIN and how does RAIN differ from other types of RFID? RAIN is a branded term for Passive Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID technology. There are five common frequency ranges that RFID technology uses: Low-Frequency (125-134 KHz), High-Frequency and NFC (13.56 MHz), Active UHF (433 MHz), Passive UHF (860-960 MHz), and .
While NFC, RFID and RAIN RFID technology may be similar, they each have clear differences. Learn more about what technology is right for your business! When customers think of paying for their lunch with their phone or smartwatch, it seems like a relatively novel concept.
The word RAIN—an acronym derived from RAdio frequency IdentificatioN—is intended as a nod to the link between UHF RFID and the cloud, where RFID-based data can be stored, managed, and shared via the Internet.Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a form of wireless communication that uses radio waves to identify and find objects. RFID is a generic term that encompasses different frequencies and standards, including both NFC and RAIN — two technologies supported by industry alliances.
what does a smart card look like
rain rfid standard
rain rfid reader
Host and manage packages Security. Find and fix vulnerabilities
rain vs rfid|impinj rfid software