rfid frequency uhf Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a See more EMV is the payment technology used by all credit cards and debit cards that have an embedded chip, which lets the cardholder more securely .About Credit Card Reader NFC (EMV) 5.5.6. This app was designed to allow users to read the public data stored on their NFC-compliant EMV banking cards, such as credit cards. EMV .
0 · ultra high frequency uhf rfid
1 · ultra high frequency rfid tags
2 · ultra high frequency rfid
3 · uhf rfid frequency by country
4 · uhf rfid definition
5 · radio frequency identification rfid system
6 · radio frequency identification rfid reader
7 · how does uhf rfid work
This quick video shows how to check whether your Android device has NFC, and whether it's enabled.Here are the steps:1. Open the Settings app on your device2.
ultra high frequency uhf rfid
The portable system operated at 915 MHz and used 12-bit tags. This technique is used by the majority of today's UHFID and microwave RFID tags. [14] In 1983, the first patent to be associated with the abbreviation RFID was granted to Charles Walton. See moreRadio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder called a tag, a radio receiver, and a See more
ultra high frequency rfid tags
In 1945, Leon Theremin invented the "Thing", a listening device for the Soviet Union which retransmitted incident radio waves with the added audio information. Sound waves vibrated a See more
An RFID tag can be affixed to an object and used to track tools, equipment, inventory, assets, people, or other objects.RFID offers . See more
Data floodingNot every successful reading of a tag (an observation) is useful for business purposes. A large . See more
A radio-frequency identification system uses tags, or labels attached to the objects to be identified. Two-way radio transmitter-receivers called . See more
To avoid injuries to humans and animals, RF transmission needs to be controlled. A number of organizations have set standards for RFID, . See more• AS5678• Balise• Bin bug• Campus card• Chipless RFID• FASTag See more
RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the .
ultra high frequency rfid
The portable system operated at 915 MHz and used 12-bit tags. This technique is used by the majority of today's UHFID and microwave RFID tags. [14] In 1983, the first patent to be associated with the abbreviation RFID was granted to Charles Walton. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz. The operating frequency of UHF RFID is 860MHz-960MHz.
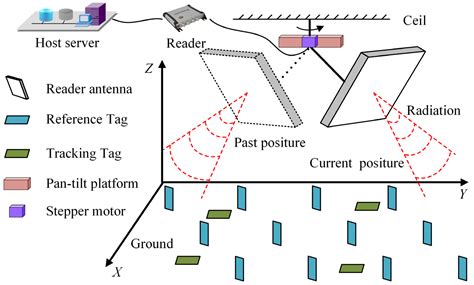
UHF (Ultra High Frequency) in RFID Frequency. UHF, or ultra-high frequency RFID, operates in the 860 MHz to 960 MHz band and is widely used, especially in logistics and supply chain management. It is popular for its long-distance reading ability and fast data transmission speed.The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID systems is typically 13.56 MHz. This is a frequency band mainly open to industrial, scientific and medical institutions and requires no licenses or fees. Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics.
Ultra-high frequency (UHF) UHF operates within the frequency range of 860 and 960 MHz, offering a reading distance of up to 12m, which varies depending on the size of the antenna. UHF operates using backscatter allowing it to recognize and read multiple tags simultaneously. UHF has the highest range of reading and writing to and from the data tags.
Ultra-high-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. This range provides even longer reading distances, typically up to 12 meters or more. UHF RFID is widely used in supply chain management, asset tracking, and retail inventory management.
While ultra-high frequencies (UHF) have a greater read range and can transmit data faster than LF and HF tags, they consume more power and are not as versatile when it comes to the types of materials that they can penetrate.The portable system operated at 915 MHz and used 12-bit tags. This technique is used by the majority of today's UHFID and microwave RFID tags. [14] In 1983, the first patent to be associated with the abbreviation RFID was granted to Charles Walton. RFID operates across three primary frequency bands: Low Frequency (LF), High Frequency (HF), and Ultra-High Frequency (UHF). In this guide, we’ll explore the characteristics of each band, their applications, and how to choose the one that best fits your needs.Learn how to choose the right RFID frequency for your system with this step-by-step guide. Explore the differences between LF, HF, and UHF, and optimize performance and cost for your RFID applications.
Generally speaking, RFID systems are mainly divided into the following three types: LF RFID, HF RFID, and UHF RFID. The operating frequency of LF RFID is 125kHz-134.2 kHz. The operating frequency of HF RFID is 13.56MHz. The operating frequency of UHF RFID is 860MHz-960MHz.UHF (Ultra High Frequency) in RFID Frequency. UHF, or ultra-high frequency RFID, operates in the 860 MHz to 960 MHz band and is widely used, especially in logistics and supply chain management. It is popular for its long-distance reading ability and fast data transmission speed.
The operating frequency of high-frequency RFID systems is typically 13.56 MHz. This is a frequency band mainly open to industrial, scientific and medical institutions and requires no licenses or fees. Typically, passive RFID systems use either low frequency (LF), high frequency (HF), or ultra-high frequency (UHF). Based on a schematic overview, this blog article provides an initial guide to these frequency ranges and their characteristics. Ultra-high frequency (UHF) UHF operates within the frequency range of 860 and 960 MHz, offering a reading distance of up to 12m, which varies depending on the size of the antenna. UHF operates using backscatter allowing it to recognize and read multiple tags simultaneously. UHF has the highest range of reading and writing to and from the data tags.Ultra-high-frequency RFID operates at frequencies between 300 MHz and 3 GHz. This range provides even longer reading distances, typically up to 12 meters or more. UHF RFID is widely used in supply chain management, asset tracking, and retail inventory management.
smart card cover

uhf rfid frequency by country
uhf rfid definition
radio frequency identification rfid system
No, you cannot use amiibo cards without the NFC Reader/Writer accessory. Amiibo cards work the same way as regular amiibo figurines and require a special .
rfid frequency uhf|how does uhf rfid work