rfid chip micro A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. SBI Card Pay uses the NFC technology to make a contactless payment that is carried out by using a smartphone at NFC enabled Point of Sale (POS) machines. You can transact up to Rs. 25,000 in a day (max. capping of up to Rs. 5,000 .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what is rfid chip
2 · what is a rfid microchips
3 · smallest rfid chip
4 · rfid chips in humans
5 · microchip tracker for humans
6 · human microchip implant handheld scanner
7 · chip for human identification
The new NFC Soundbox will enable merchants to accept payments, both above and below ₹5000. May 29, 2024. Axis Bank, one of the largest private sector banks in India, today announced the launch of NFC .
Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.
rf plastic ink pin tags
Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an .Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an entire transponder.
A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being. Sweden's largest train company has started allowing commuters to use chips instead of tickets, and there's talk that the chips could soon be used to make payments in shops and restaurants. These implants often fall under the RFID (radio-frequency identification) umbrella, and RFID technology encompasses a very broad spectrum of frequencies, devices, protocols, and interfaces.
RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an .
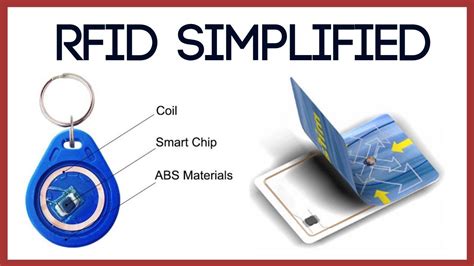
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.
A pet microchip uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. RFID, as the name implies, uses radio waves as a medium to transmit information. An RFID tag stores data and, using electromagnetic forces for power, communicates that data to a device that interprets it.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips are identifying transponders that typically carry a unique identification number and can be tagged with user data such as health records, social. The development of nano-sized RFID chips, such as the mu-chip and the Micro-Machined Chip (MMC), has demonstrated the incredible progress in miniaturization. Tiny RFID chips find applications in diverse domains, including healthcare, smart retail, asset tracking, and animal identification.Are you ready for an RFID implant? Here’s everything what you should know about RFID chips before you implant them into your body.
Our RFID chips are suitable for the smallest devices and don’t require any external components, which reduces the cost of your tag. These identification ICs are available as die-on-wafers with optional gold bumps, packaged die or an entire transponder.A human microchip implant is any electronic device implanted subcutaneously (subdermally) usually via an injection. Examples include an identifying integrated circuit RFID device encased in silicate glass which is implanted in the body of a human being.
Sweden's largest train company has started allowing commuters to use chips instead of tickets, and there's talk that the chips could soon be used to make payments in shops and restaurants. These implants often fall under the RFID (radio-frequency identification) umbrella, and RFID technology encompasses a very broad spectrum of frequencies, devices, protocols, and interfaces. RFID microchips, embedded under the skin with a procedure that’s already cheap and available, provide a digital interface to the real world centered about the holder’s identity: your ID, credit card information, bus pass, library card, and many other sources of information you currently carry in your purse/wallet can instead be stored on an . An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings.
A pet microchip uses radio frequency identification (RFID) technology. RFID, as the name implies, uses radio waves as a medium to transmit information. An RFID tag stores data and, using electromagnetic forces for power, communicates that data to a device that interprets it.
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) chips are identifying transponders that typically carry a unique identification number and can be tagged with user data such as health records, social.
where are rfid chips used
what is rfid chip
Just like the regular EMV-Contactless chip, the signal sent by the NFC from the mobile device is only valid for a one-time usage. The cryptogram ensures that the same data can’t be charged twice and the transaction value .
rfid chip micro|microchip tracker for humans