rfid vs nfc reader RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field . Using an NFC Reader/Writer accessory you can use amiibo on your Nintendo 3DS or Nintendo 2DS. Learn more in this video.Official site: https://www.nintend.
0 · rfid vs nfc difference
1 · rfid nfc reader writer
2 · nfc tag reader used for
3 · nfc rfid reader software
4 · nfc rfid reader app
5 · differences between rfid and nfc
6 · adafruit rfid reader
7 · adafruit nfc reader
Brothership is the sixth mainline installment in the Mario & Luigi. Analogue will .
how to download e-smart ration card online tnpds.gov.in
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field .
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security. NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. Let’s compare the two, side by side, to better understand where they overlap and what makes them different.
how to find smart ration card number in tamilnadu
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.This blog will provide an in-depth look at how RFID vs NFC work and the key differences between them to help users make informed choices when deploying the technologies.Cost and Infrastructure: Security and Privacy: User Experience and Adoption: Understanding RFID technology. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects or people. At its core, an RFID system consists of three main components: a tag (or transponder), a reader, and an antenna.RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not .
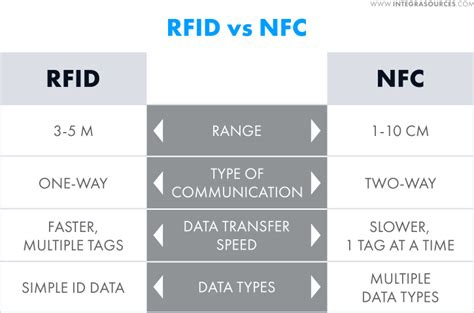
While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.However, there is a distinction between the two. Unlike RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) tags, NFC tags have the capability to both send and receive information, allowing for two-way communication. In contrast, RFID tags are typically designed for one-way communication.
NFC stands for near field communication, while RFID means radio frequency identification. Both employ radio signals for all sorts of tagging and tracking purposes, sometimes replacing bar codes. NFC is still an emerging technology; RFID, however, is currently in . RFID is more widely applicable across the supply chain, but near-field communication (NFC) has applications in manufacturing settings and can deliver information to retail consumers, among other applications. Other key differences between the technologies include cost and security. NFC is best used to securely transfer a range of data over short distances, hence its prevalence in access control and payment applications. On the other hand, RFID is more suited to faster moving environments with lots of moving parts and is most often used for vehicle access control and asset management purposes.When it comes down to it, NFC is a type of RFID. So, while all NFC is considered RFID, not all RFID is NFC. Let’s compare the two, side by side, to better understand where they overlap and what makes them different.
RFID is the process by which items are uniquely identified using radio waves, and NFC is a specialized subset within the family of RFID technology. Specifically, NFC is a branch of High-Frequency (HF) RFID, and both operate at the 13.56 MHz frequency.This blog will provide an in-depth look at how RFID vs NFC work and the key differences between them to help users make informed choices when deploying the technologies.
Cost and Infrastructure: Security and Privacy: User Experience and Adoption: Understanding RFID technology. RFID, or Radio Frequency Identification, is a technology that uses radio waves to identify and track objects or people. At its core, an RFID system consists of three main components: a tag (or transponder), a reader, and an antenna.
RFID’s ultra-high frequency technology can read multiple tags in batches at a long distance, greatly improving the efficiency of logistics and inventory management, while NFC is not . While RFID excels in large-scale, long-distance scanning, NFC offers more versatile data storage and access, with the added benefit that most modern smartphones can read NFC tags without the need for expensive readers.
rfid vs nfc difference
rfid nfc reader writer
nfc tag reader used for
ACR1552. The ACR1552U USB NFC Reader IV is a CCID and PC/SC compliant smart card reader, meticulously developed utilizing advanced 13.56MHz contactless technology. This innovative device is designed to offer seamless .
rfid vs nfc reader|rfid vs nfc difference