how small are rfid chips As a result, today’s RFID chips can be as small as a grain of rice or even smaller. Some manufacturers have managed to develop RFID chips that measure only a few millimeters on each side. I just bought some NFC tags and my new iphone 12 pro reads them through 3rd .
0 · where are rfid chips used
1 · what makes something rfid
2 · what does rfid look like
3 · types of rfid chips
4 · rfid is involved when using
5 · rfid for personal use
6 · how does rfid scanning work
7 · how do rfid chips work
Auburn is favored to pick up the win over Auburn according to ESPN Bet. Here is the spread, money lines and over/under as of Friday morning. Spread: Auburn (-24.5) Moneylines: .The Kick Six (also known as Kick Bama Kick) was the final play of the 78th Iron Bowl college football game played on November 30, 2013, at Jordan–Hare Stadium in Auburn, Alabama. The game featured the No. 1-ranked and two-time defending national champion Alabama Crimson Tide (11–0, 7–0 in the SEC) . See more
As a result, today’s RFID chips can be as small as a grain of rice or even smaller. Some manufacturers have managed to develop RFID chips that measure only a few millimeters on each side.
As a result, today’s RFID chips can be as small as a grain of rice or even smaller. Some manufacturers have managed to develop RFID chips that measure only a few millimeters on each side.
Standard size: These RFID chips are usually between 3 and 5 cm in size and are widely used in logistics, inventory management and asset tracking. Their larger size allows longer antennas, providing longer reading distances and better signal transmission stability.
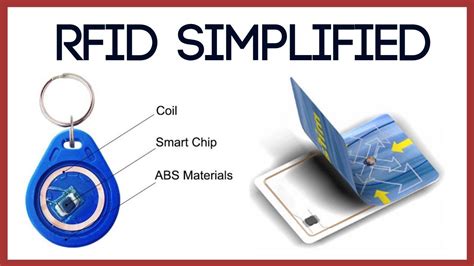
An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies. LF RFID chips have a frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, they typically operate on frequencies between 125 kHz and 132 kHz. Most of the Low-frequency tags are passive tags that obtain energy from the radiation near the field of the reader coupling coil by inductive coupling. RFID technology is the wireless technology used to identify and track objects using radio waves. An RFID tag is a part of RFID technology. It is a small device that contains a microchip and an antenna, which work together to transmit .
Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips. Researchers are the University of Stanford running a project of developing a 60GHZ passive RFID tag that is as small as to fit in a human body cell. The team of developers has managed to scale down the size of the antenna and the chip to 22 microns (that is about 0.0009 inches) wide.
RFID chips are integrated circuits inside RFID tags. They are small, highly integrated microchips that contain a logical control unit, memory, and transceiver for decoding, decrypting, and error checking.With the advancement of chip manufacturing technology, chips can be made very small. Antenna design: The shape and size of the antenna directly affect the performance of the tag. An antenna of a certain length is the key to maintaining a good reading distance. As a result, today’s RFID chips can be as small as a grain of rice or even smaller. Some manufacturers have managed to develop RFID chips that measure only a few millimeters on each side.
Standard size: These RFID chips are usually between 3 and 5 cm in size and are widely used in logistics, inventory management and asset tracking. Their larger size allows longer antennas, providing longer reading distances and better signal transmission stability. An RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) chip is a small device that uses radio waves to transmit data wirelessly. It consists of a microchip and an antenna, encapsulated in a tiny package. These chips are often embedded in various items, such as cards, tags, labels, or even implanted in living beings. Researchers at North Carolina State University have made what is believed to be the smallest state-of-the-art RFID chip, which should drive down the cost of RFID tags. In addition, the chip’s design makes it possible to embed RFID tags into high value chips, such as computer chips, boosting supply chain security for high-end technologies. LF RFID chips have a frequency range of 30 kHz to 300 kHz. However, they typically operate on frequencies between 125 kHz and 132 kHz. Most of the Low-frequency tags are passive tags that obtain energy from the radiation near the field of the reader coupling coil by inductive coupling.
read rfid card data
RFID technology is the wireless technology used to identify and track objects using radio waves. An RFID tag is a part of RFID technology. It is a small device that contains a microchip and an antenna, which work together to transmit .Researchers at North Carolina State University have created what they say is the smallest-ever second-generation radio-frequency identification (RFID) chip — paving the way to lower-cost RFID tags and tags embeddable in new devices, including silicon chips.
Researchers are the University of Stanford running a project of developing a 60GHZ passive RFID tag that is as small as to fit in a human body cell. The team of developers has managed to scale down the size of the antenna and the chip to 22 microns (that is about 0.0009 inches) wide.
RFID chips are integrated circuits inside RFID tags. They are small, highly integrated microchips that contain a logical control unit, memory, and transceiver for decoding, decrypting, and error checking.
rasberry pai rfid reader
where are rfid chips used
what makes something rfid
read rfid tag with phone
Using an ACR122 device with libnfc and without tag (e.g. to use NFCIP modes or card emulation) needs yet another PCSC-lite tweak: You need to allow usage of CCID Exchange command.
how small are rfid chips|how does rfid scanning work